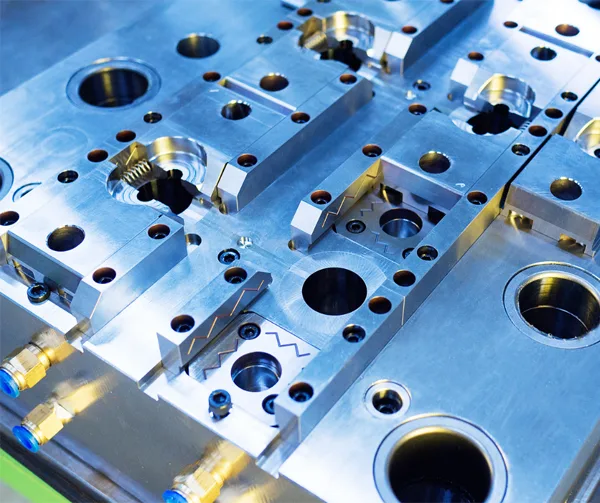
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern manufacturing, the demand for perfection is not just a goal; it is a baseline requirement. Whether it is the intricate internal components of a medical device, the high-conductivity connections in an Electric Vehicle (EV) battery pack, or the structural integrity of aerospace sensors, the manufacturing world relies heavily on one critical process: precision die and stamping.
At JUMAI TECH, we have spent years refining the art and science of metal deformation. We understand that when a client requests a component, they aren’t just buying a piece of metal; they are investing in reliability, efficiency, and engineering excellence. This comprehensive guide will explore the depths of precision die and stamping, specifically focusing on how we achieve tight-tolerance results for deep-drawn components, precision copper busbars, and complex stamped parts.
Table of Contents
The Fundamentals of Precision Die and Stamping
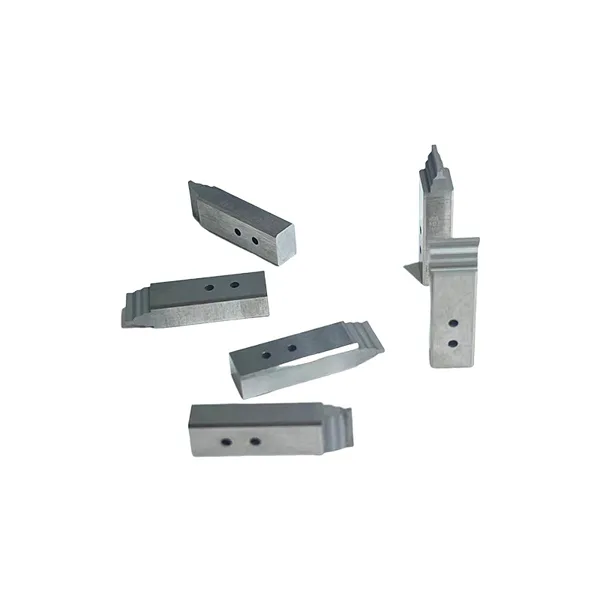

To truly appreciate the complexity of precision die and stamping, one must first distinguish it from standard metal stamping. While standard stamping often focuses on high-volume production where loose tolerances (e.g., +/- 0.5mm) are acceptable, precision stamping is a discipline defined by microscopic accuracy. It involves transforming flat metal sheets into complex three-dimensional shapes with tolerances often measured in microns.
What Defines “Precision”?
In our industry, “precision” is not a buzzword; it is a measurable metric. It refers to the ability to produce parts that deviate minimally from the nominal design specifications. This involves controlling variables such as material thickness, springback, burr height, and flatness.
For high-end applications, such as the Precision Copper Busbars we manufacture at JUMAI TECH, precision means ensuring that the contact surfaces are perfectly flat to maximize electrical conductivity and minimize heat generation. A deviation of even a fraction of a millimeter can lead to increased resistance, thermal hotspots, and eventual system failure. Therefore, precision die and stamping is as much about risk management as it is about metalworking.
The Role of the Die
The “die” is the heart of the stamping process. It is a specialized tool, custom-designed and machined to cut, bend, and shape metal. In precision stamping, the die is often made from hardened tool steel or carbide to withstand millions of cycles without losing dimensional accuracy.
There are several types of dies used in our facility, each serving a specific purpose:
- Progressive Dies: These are used for high-speed, high-volume production. The metal strip feeds through multiple stations, with each station performing a specific operation (cutting, bending, punching) until the finished part is ejected at the end.
- Compound Dies: These perform multiple operations (like cutting and punching) in a single stroke, ensuring excellent concentricity and flatness.
- Deep Draw Dies: These are specifically designed to stretch metal into cup-like shapes, a core competency of JUMAI TECH.
According to the Precision Metalforming Association (PMA), the choice of die design is the single most critical factor in determining the cost-efficiency and quality of the final stamped component.
Achieving Tight Tolerances: The Engineering Behind the Process
Achieving tight tolerances in precision die and stamping requires a symbiotic relationship between advanced machinery, material science, and expert engineering. It is not enough to simply apply force to metal; one must understand how the metal will react to that force.
Material Memory and Springback
One of the greatest challenges in stamping is “springback.” When metal is bent, it has a natural tendency to return to its original shape slightly after the force is removed. This elastic recovery can compromise the dimensional accuracy of the part.
In the production of our Precision Stamping Dies, our engineers utilize advanced simulation software to calculate the exact amount of springback for specific materials, such as Beryllium Copper or Stainless Steel. We then design the die to “over-bend” the material slightly, so that when it springs back, it settles into the exact required angle. This is particularly crucial for complex geometries found in automotive connectors and electronic shielding.
The Importance of Press Rigidity
The stamping press itself plays a vital role. For tight-tolerance components, we utilize presses with high rigidity and minimal deflection. If a press frame flexes under the tonnage load, the die alignment shifts, leading to inconsistent parts and premature tool wear.
At JUMAI TECH, our facility is equipped with high-tonnage presses that feature active vibration dampening and thermal compensation systems. This ensures that even as the machine heats up during a long production run, the precision die and stamping process remains stable, maintaining tolerances as tight as +/- 0.01mm.
Comparison of Stamping Methods
To understand where precision stamping fits, it is helpful to compare it with other manufacturing methods. The table below illustrates why precision stamping is often the preferred choice for high-volume, high-accuracy components.
| Feature | Precision Stamping | CNC Machining | Metal Casting |
| Production Speed | Extremely High | Low to Medium | Medium |
| Material Waste | Low (Optimized Nesting) | High (Subtractive) | Medium |
| Tolerance Capability | High (+/- 0.01mm) | Very High (+/- 0.005mm) | Low to Medium |
| Cost Per Unit (Volume) | Very Low | High | Medium |
| Strength/Grain Flow | Improved (Work Hardening) | Interrupted Grain | Isotropic |
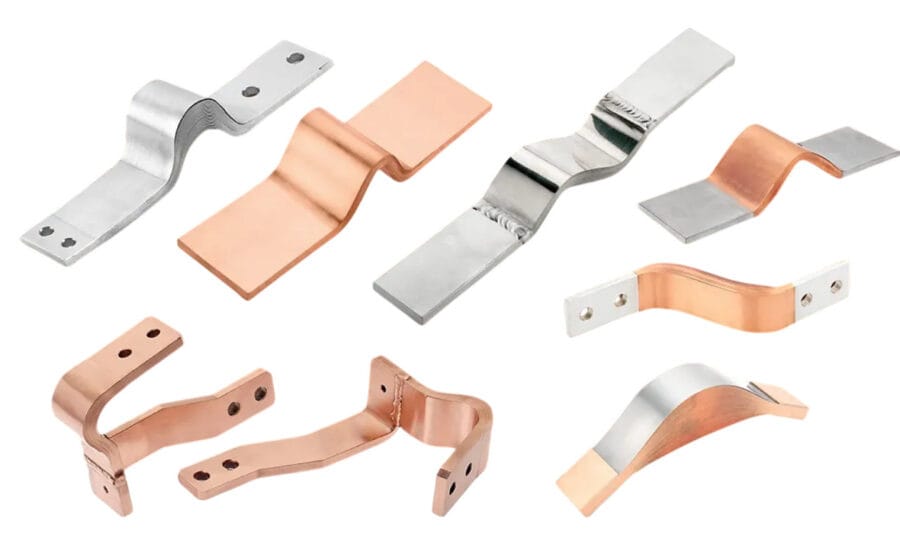
Deep-Drawn Components: A JUMAI TECH Specialty
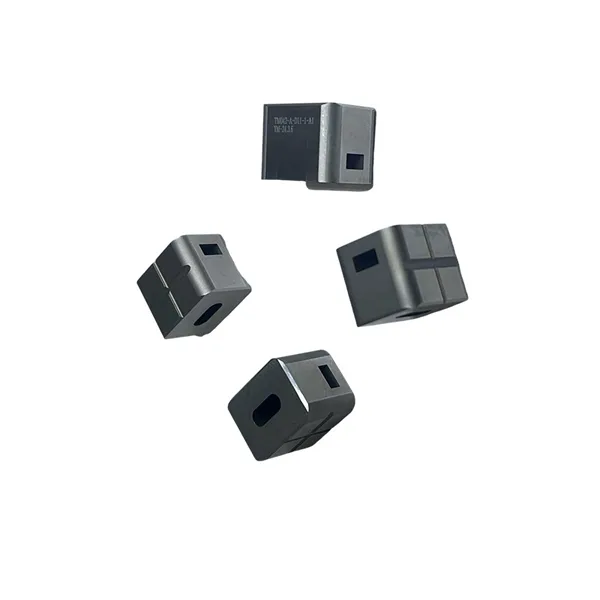

While standard stamping deals with cutting and folding, deep drawing is a transformative process. It involves pulling a metal blank into a die cavity to create a hollow shape where the depth exceeds the diameter. This is a sub-segment of precision die and stamping that requires exceptional control over material flow.
The Physics of Deep Drawing
Deep drawing subjects the material to extreme tension and compression simultaneously. The flange of the blank is compressed as it is drawn into the die, while the wall of the cup is under tension. If the process is not controlled perfectly, the material can wrinkle, tear, or thin out excessively.
We utilize multi-stage transfer presses for our Deep-Drawn Components. This allows us to draw the metal in gradual steps, reducing stress on the material and preventing fractures. This capability is essential for manufacturing battery cans, sensor housings, and capacitor cases used in industrial electronics.
Ironing and Wall Thickness Control
A critical aspect of high-precision deep drawing is “ironing.” This is a process where the wall of the drawn part is thinned and lengthened to achieve a uniform thickness and a highly polished surface finish.
For clients requiring hermetic seals or precise internal volumes, ironing ensures that the component meets strict specifications. Unlike standard stamping, which may leave rough edges, our deep-drawn and ironed parts often require no secondary finishing, saving our customers time and money.
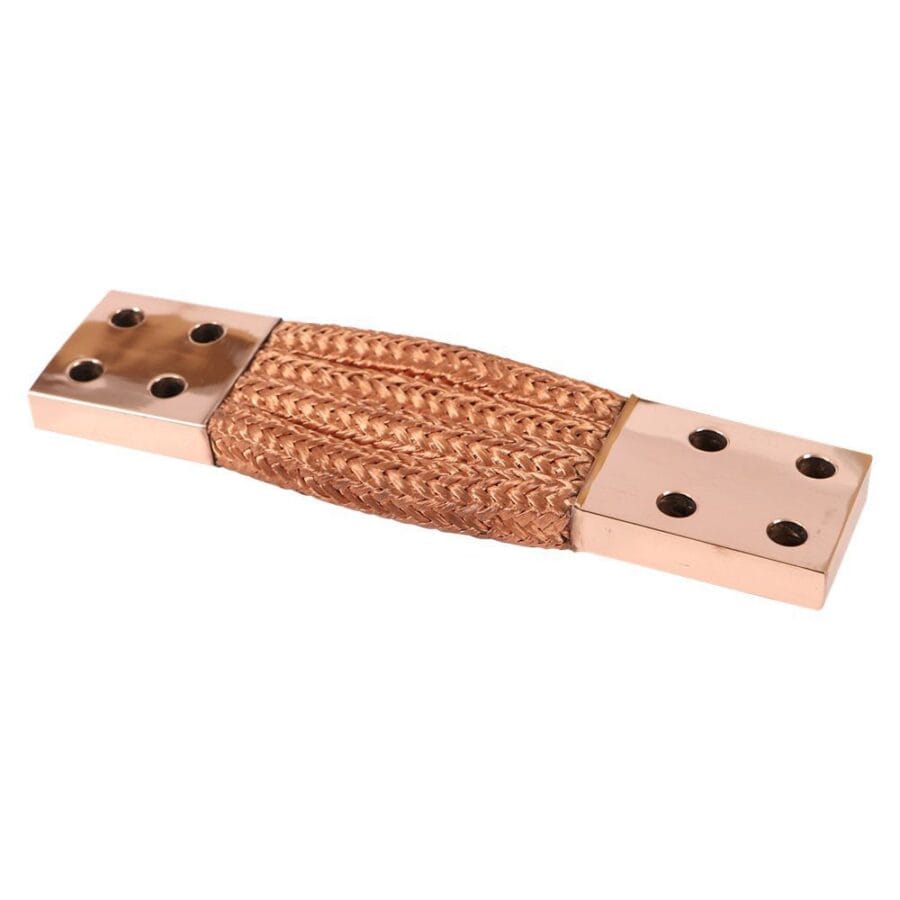
Precision Copper Busbars: Powering the Future
A significant portion of our work at JUMAI TECH involves the fabrication of Precision Copper Busbars. As the world shifts towards electrification, the demand for efficient power distribution systems has skyrocketed. Busbars are the backbone of these systems, and their manufacturing relies heavily on precision die and stamping techniques.
Why Stamping for Busbars?
Traditionally, busbars were machined or cut using waterjets. However, for high-volume automotive and energy storage applications, stamping offers superior consistency. We use precision dies to punch holes, form bends, and emboss contact points in a single continuous process.
Stamping copper presents unique challenges because copper is highly ductile and “gummy.” It tends to stick to the punch, leading to burrs. Our engineers utilize specialized coatings on our punches and dies (such as TiCN or DLC coatings) to reduce friction and ensure clean, burr-free cuts. This is vital because any burr on a high-voltage busbar can create a point of arcing or interfere with assembly.
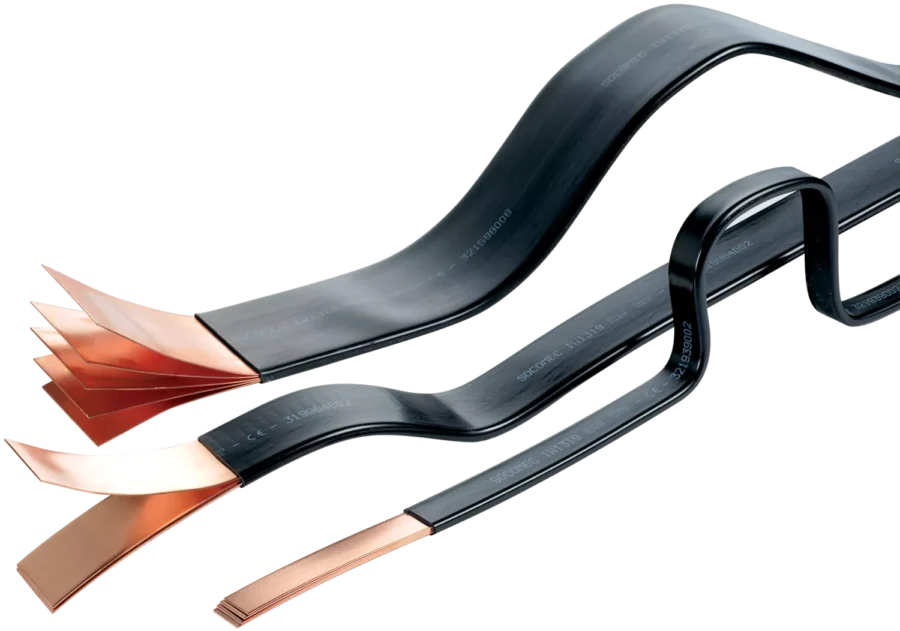
Advanced Insulation and Assembly
Beyond the metalworking, JUMAI TECH integrates insulation solutions directly into the stamping workflow. Whether it is powder coating, heat-shrink tubing, or lamination, our precision processes ensure that the insulation is applied without compromising the geometric tolerances of the copper conductor.
We also employ “in-die tapping” and “in-die assembly” technologies. This means that we can insert nuts, studs, or fasteners into the busbar while it is still in the stamping press. This eliminates secondary assembly steps and ensures that every fastener is positioned with robotic accuracy.
The Role of Tooling: Precision Stamping Dies
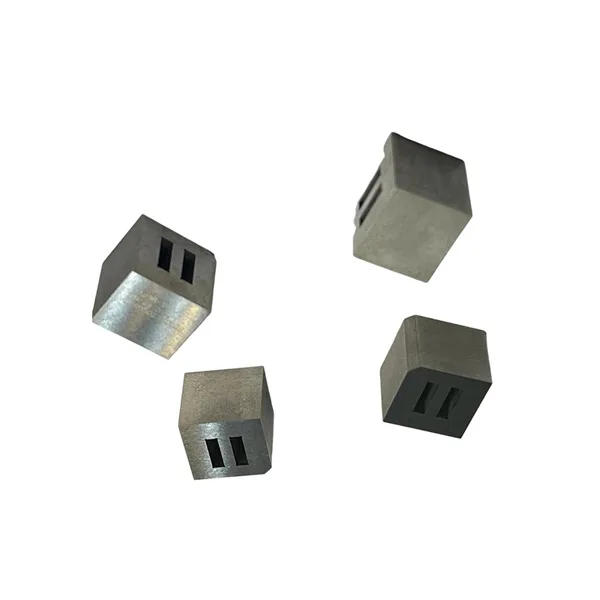

The adage “you are only as good as your tools” is absolute truth in our industry. The quality of the Precision Stamping Dies determines the quality of the final part. At JUMAI TECH, we do not just use dies; we design and manufacture them in-house.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Before a single piece of steel is cut, our engineering team engages in Design for Manufacturability (DFM). We analyze the client’s part design to identify potential issues that could arise during stamping. For example, if a hole is too close to a bend, it will deform. If a tolerance is unnecessarily tight for a non-critical feature, it will drive up cost without adding value.
By optimizing the design for the precision die and stamping process, we can often reduce material usage by 10-15% and extend the life of the tooling. This collaborative approach is what sets JUMAI TECH apart as a partner rather than just a vendor.
Wire EDM and CNC Machining
To build dies capable of micron-level precision, we utilize Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (Wire EDM). This process uses an electrically charged wire to cut through hardened steel with incredible accuracy. It allows us to create complex die geometries that would be impossible with traditional machining.
According to data from SME (Society of Manufacturing Engineers), the use of advanced EDM technology in die making has improved achievable tolerances by over 40% in the last decade. We leverage this technology to ensure that every punch and matrix in our dies fits together with zero clearance where necessary, ensuring the cleanest possible cut on the metal strip.
Material Science in Precision Stamping
Selecting the right material is a critical decision in precision die and stamping. The material must not only meet the functional requirements of the final part (e.g., strength, conductivity, corrosion resistance) but also possess the formability required for the stamping process.
Copper and Copper Alloys
As experts in Precision Copper Busbars, we work extensively with C11000 (ETP) and C10200 (Oxygen-Free) copper. These materials offer excellent conductivity but require careful handling to prevent work hardening during the forming process. We also utilize high-performance copper alloys like Beryllium Copper and Phosphor Bronze for spring contacts, where the material must maintain elasticity over millions of cycles.
Stainless Steel and Exotic Alloys
For our Deep-Drawn Components, Stainless Steel (304, 316L) is a popular choice due to its corrosion resistance and strength. However, stainless steel work-hardens rapidly, meaning it becomes harder and more brittle the more you deform it.
To counter this, we employ intermediate annealing processes for deep-drawn parts. This involves heating the manufacturing part to relieve internal stresses before continuing the drawing process. This allows us to achieve draw ratios that exceed standard industry capabilities.
Data on Material Formability
The table below highlights the “n-value” (work hardening exponent) and “r-value” (anisotropy) of common materials we use. Higher n-values generally indicate better stretchability, while higher r-values indicate better deep drawability.
| Material | Alloy Grade | Typical n-value | Typical r-value | Application |
| Low Carbon Steel | 1008/1010 | 0.20 – 0.23 | 1.4 – 1.8 | General Stamping |
| Stainless Steel | 304 | 0.40 – 0.50 | 1.0 | Deep Drawn Cans |
| Copper | C11000 | 0.35 – 0.45 | 0.6 – 0.9 | Busbars, Contacts |
| Aluminum | 5052-O | 0.25 – 0.30 | 0.6 – 0.8 | Lightweight Housings |
Quality Control and Metrology
In the world of precision die and stamping, you cannot manage what you cannot measure. Quality control is not the final step at JUMAI TECH; it is integrated into every stage of production.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
We utilize Statistical Process Control (SPC) to monitor our production in real-time. By measuring a sample of parts at regular intervals, we can detect trends before they become issues. For example, if we notice that a dimension is slowly drifting toward the upper tolerance limit, it may indicate that the die punch is wearing down. We can then pause production and service the tool before any bad parts are made.
Our target is typically a Cpk (Process Capability Index) of 1.33 or higher, which statistically guarantees that 99.99% of parts are within specification. For automotive clients, we often aim for a Cpk of 1.67.
Automated Vision Inspection
For high-volume components, manual inspection is impossible. We employ automated optical inspection (AOI) systems that photograph every single part coming off the press. These systems use advanced algorithms to check for dimensions, surface scratches, missing features, and burrs.
This technology allows us to guarantee zero-defect shipments for critical components. When a client receives a shipment of Precision Stamping Dies accessories or stamped parts from JUMAI TECH, they can trust that every unit is compliant.
Industries Served by JUMAI TECH
The versatility of precision die and stamping allows us to serve a diverse range of industries. Each sector has unique requirements, and our adaptability is key to our success.
Automotive and EV Revolution
The automotive industry is undergoing a seismic shift toward electrification. This has created a massive demand for our Precision Copper Busbars and high-voltage connectors. These components must carry high currents while withstanding the vibration and thermal cycling of a vehicle environment. Our precision stamping ensures that the grain structure of the copper remains intact, maximizing fatigue life.
Telecommunications and 5G
The rollout of 5G infrastructure requires millions of small, complex metal components for antennas, shielding cans, and heat sinks. These parts often require tight tolerances to ensure proper signal integrity. Our deep-drawn components are ideal for these applications, providing seamless, leak-proof enclosures for sensitive electronics.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, failure is not an option. We manufacture surgical instrument components, device housings, and implantable battery cases. For these applications, we utilize medical-grade stainless steel and titanium. Our cleanroom-compatible cleaning processes ensure that parts are free from oil and particulate contamination.
Cost Optimization Strategies
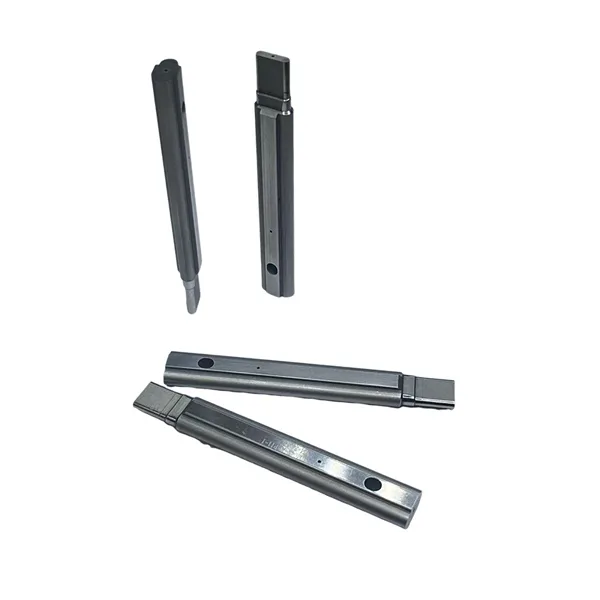

One of the misconceptions about precision die and stamping is that it is prohibitively expensive. While the initial tooling cost can be significant, the piece price drops dramatically as volume increases. However, there are ways to optimize costs even further.
Material Utilization
Material cost often makes up 60-70% of the total part cost. Our engineers use nesting software to arrange the parts on the metal strip in a way that minimizes scrap. For expensive materials like copper and silver-plated alloys, reducing scrap by even 5% can save thousands of dollars per production run.
Modular Tooling Design
To lower the barrier to entry for our clients, we often employ modular die designs. This allows us to swap out specific inserts in a master die base to produce different versions of a part. Instead of building a completely new die for a slightly longer busbar or a deeper can, we simply change the relevant inserts. This significantly reduces tooling lead time and cost.
Speed vs. Quality Balance
Running a press at maximum speed isn’t always the most efficient option if it leads to higher reject rates. We analyze the “sweet spot” for each specific precision die and stamping job. By optimizing the stroke rate, we maximize tool life and part consistency, which ultimately lowers the total cost of ownership for our clients.
Why Partner with JUMAI TECH?
In a global market flooded with manufacturers, JUMAI TECH stands out by adhering to a philosophy of “Precision without Compromise.” Our website, www.deepdrawtech.com, is not just a showcase; it is a testament to our capabilities in Precision Copper Busbars, Deep-Drawn Components, and Precision Stamping Dies.
Full-Service Capability
We are not just a stamping house; we are a solution provider. From the initial concept and prototype to mass production and logistics, we handle every step. Our in-house tool shop allows us to react quickly to design changes and maintain our dies without relying on third-party vendors.
Global Logistics
Serving global clients requires more than just manufacturing skills; it requires logistical expertise. We are experienced in export regulations, specialized packaging for delicate electronic components, and Just-In-Time (JIT) delivery protocols. Whether you are in Europe, North America, or Asia, JUMAI TECH ensures your parts arrive on time and in perfect condition.
Commitment to Sustainability
We are also committed to sustainable manufacturing. All our scrap metal is 100% recycled. We utilize eco-friendly lubricants and cleaning solutions in our precision die and stamping processes. By optimizing material usage, we not only save money but also reduce the carbon footprint of every part we produce.
Conclusion
The world of precision die and stamping is complex, demanding, and absolutely essential to modern technology. From the Precision Copper Busbars that drive electric vehicles to the Deep-Drawn Components that house critical sensors, the need for tight-tolerance manufacturing has never been greater.
At JUMAI TECH, we combine decades of experience with cutting-edge technology to deliver results that exceed expectations. We understand the intricacies of die design, the science of material behavior, and the rigorous demands of global quality standards.
If you are looking for a partner who understands that “close enough” is never good enough, we invite you to explore our capabilities. Let us help you turn your complex designs into tangible, high-precision realities.
Contact JUMAI TECH today at www.deepdrawtech.com to discuss your next project.